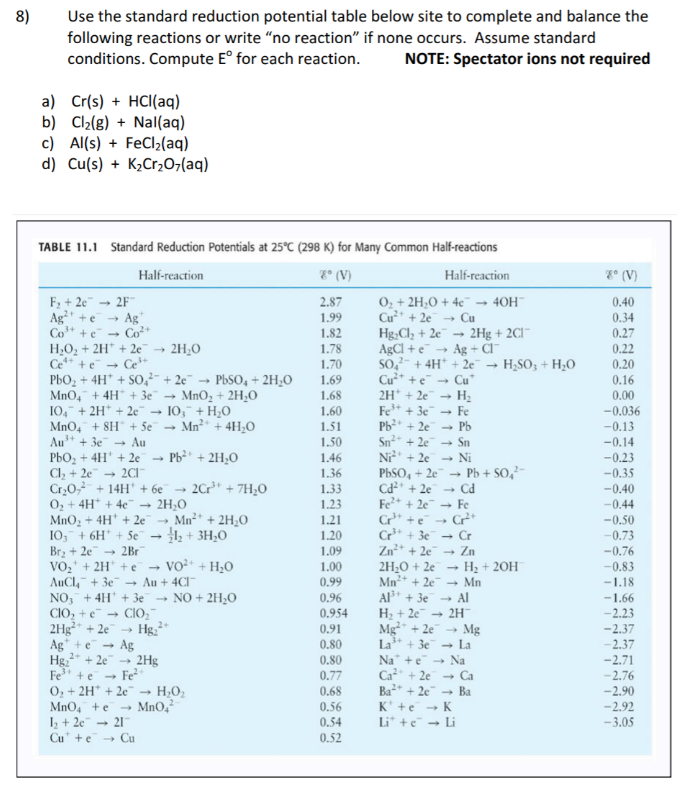
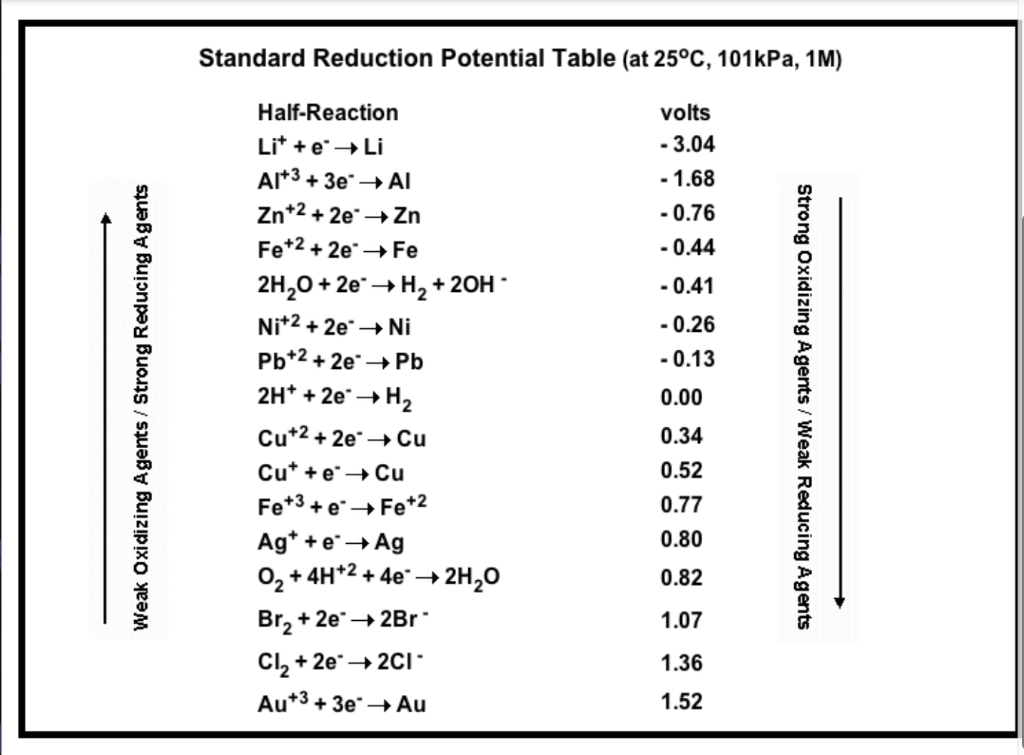
OneClass: Standard reduction potentials Use the table of standard reduction potentials given above to...

Using the standard electrode potentials given in the table, predict if the reaction between the following is possible. Ag^+(aq) and Cu(s)
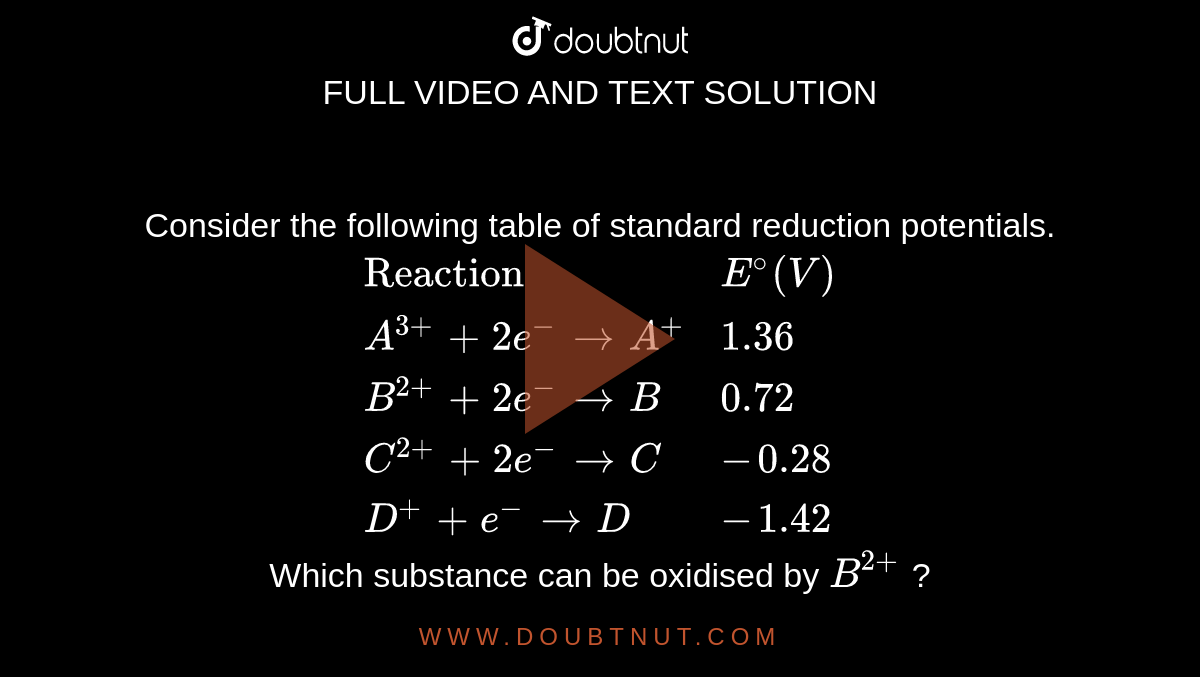
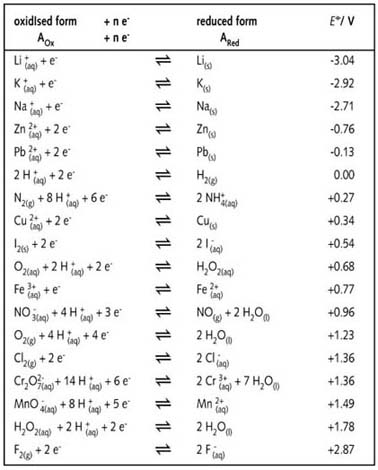
Consider the following table of standard reduction potentials. {:("Reaction",E^@(V)),(A^(3+)+2e^(-) rarrA^+,1.36),(B^(2+)+2e^(-)rarrB,0.72),(C^(2+)+2e^(-)rarrC,-0.28),(D^(+)+e^(-)rarrD,-1.42):} Which substance can be oxidised by B^(2+) ?
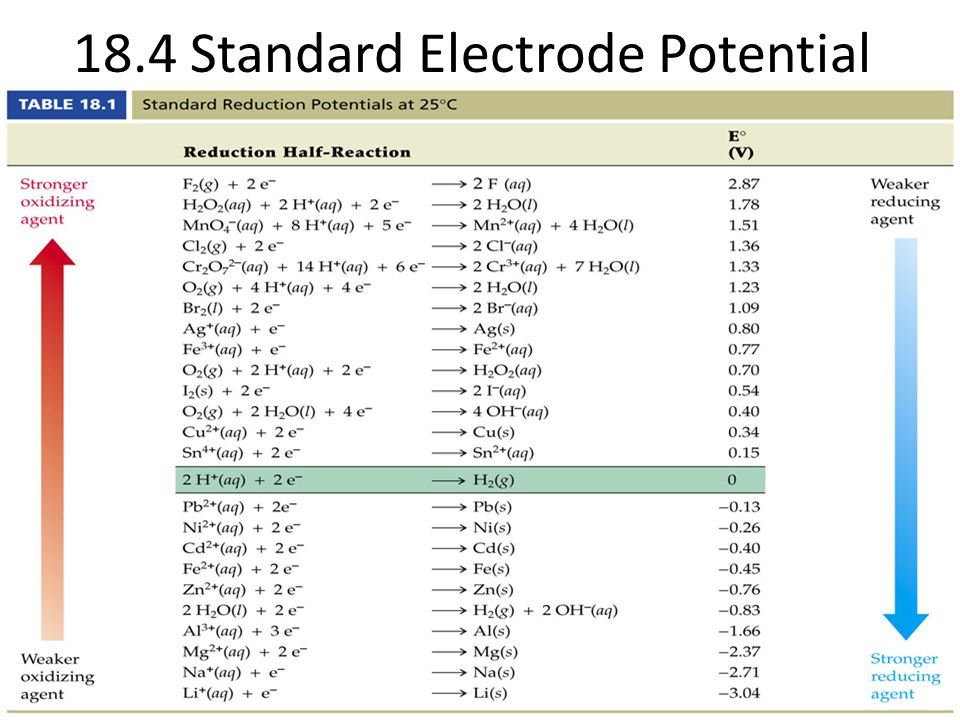
![PDF] Standard Electrode Potentials and Temperature Coefficients in Water at 298.15 K | Semantic Scholar PDF] Standard Electrode Potentials and Temperature Coefficients in Water at 298.15 K | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/56964684a624c5af38c7e62256db3faa4c542d88/19-Table2-1.png)
PDF] Standard Electrode Potentials and Temperature Coefficients in Water at 298.15 K | Semantic Scholar

Table of Standard reduction potentials.pdf - Table of Standard reduction potentials Half reaction + Li + e Li(s) K+ + e K(s) Ca2+ + 2e Ca(s) Na+ + e | Course Hero

Using the standard electrode potentials given in the table, predict if the reaction between the following is possible. Ag^+(aq) and Cu(s)
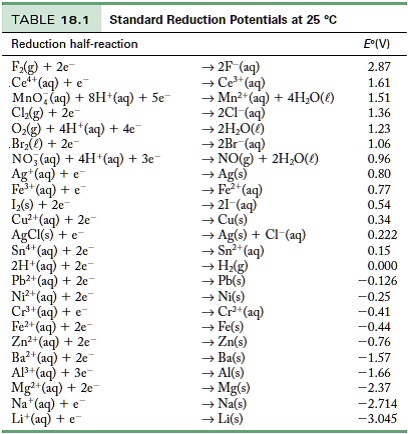

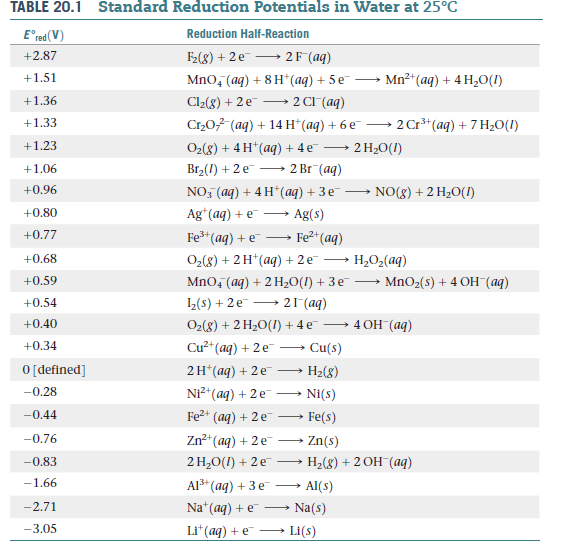





![Standard reduction potentials at 298°K. [24] | Download Table Standard reduction potentials at 298°K. [24] | Download Table](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/316026333/figure/tbl2/AS:650784626708491@1532170554986/Standard-reduction-potentials-at-298K-24.png)